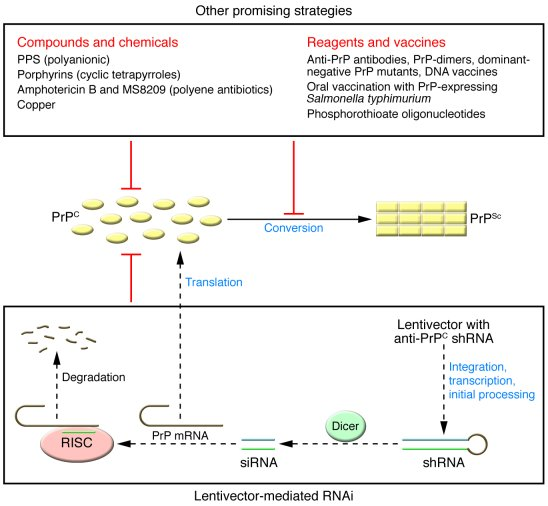
Prion disease treatment has taken a significant leap forward, capturing the attention of researchers and patients alike, as recent studies unveil promising advancements in therapy. Conditions such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia exemplify the severe impact these rare disorders have on individuals and their families, sparking a fervent quest for effective solutions. The groundbreaking work led by scientists at the Broad Institute has introduced innovative gene editing techniques aimed at addressing the underlying causes of prion diseases. This research not only highlights the potential for developing prion therapy advancements but also reflects the personal stakes faced by patient-scientists working tirelessly to find a cure. As prion protein research continues to evolve, the excitement and hope surrounding treatment possibilities signal a new era for those affected by these devastating conditions.
The quest for therapies targeting prion diseases has gained momentum, with numerous initiatives exploring ways to combat these rare and life-threatening ailments. Disorders like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia share a common thread of protein misfolding, which leads to severe neurodegenerative consequences. In recent months, inventive strategies involving gene editing for prion disease have emerged, providing a glimpse of hope in the landscape of medical research. Collaborations among dedicated scientists and patient advocates underscore the urgency and importance of these developments, as they seek solutions to alleviate the toll of prion-related illnesses. With advancements in prion therapy, the future holds promise for achieving better outcomes for individuals impacted by these tragic conditions.
Understanding Prion Diseases: Types and Impacts
Prion diseases are a group of rare, progressive neurodegenerative disorders characterized by misfolded proteins in the brain that lead to severe neurological impairment and death. Notable examples include Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, a condition that can develop spontaneously or through exposure, and fatal familial insomnia, an inherited disorder that disrupts sleep and cognitive functions. These diseases are particularly alarming due to their invariably fatal outcomes and the profound impact they have on patients and their families. As researchers analyze the genetic mutations linked to these diseases, including those responsible for inherited forms, the scientific community gains a clearer understanding of how these devastating conditions unfold.
In addition to the well-known Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, fatal familial insomnia exemplifies the urgency of prion disease research. Characterized by severe sleep disturbances and neurodegeneration, it underscores the complexity of prion diseases. The understanding of these conditions is vital for developing therapies, as they not only affect the patients but also place emotional and psychological burdens on families. Therefore, advancements in prion protein research and therapies are crucial to alleviate these burdens and pave the way for hope in affected families.
Promising Advances in Prion Disease Treatment
Recent research has highlighted significant advancements in prion disease treatment, particularly through groundbreaking gene-editing techniques aimed at mitigating the production of toxic prion proteins. The development of gene-editing therapies, such as base editing, offers hope for a new avenue to combat conditions like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia. By altering the genetic sequence responsible for producing harmful prion proteins, it’s possible to reduce their levels significantly, as evidenced by studies demonstrating lifespan extensions in murine models. These advances reflect a critical milestone towards finding effective treatments for devastating prion diseases.
The collaborative efforts of researchers, particularly patient-scientists like Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel, bring a unique perspective to prion therapy advancements. Their personal stakes in the research drive not just the scientific inquiry but also the urgency for practical applications. As their lab works closely with others, continuously refining experimental approaches following successful genetic modifications, the scientific community anticipates more collaborative projects that could lead to swift progress in human applications. Each step taken contributes to the achievable goal of developing a solid therapeutic option for patients suffering from these life-threatening illnesses.
The Intersection of Gene Editing and Prion Proteins in Research,
Gene editing has emerged as a transformative approach in the research of prion diseases, allowing scientists to tackle the underlying genetic causes with unparalleled precision. Using technologies like CRISPR and base editing, researchers are modifying the genes responsible for producing harmful prion proteins. This method has shown promising results in laboratory settings, such as reducing the levels of these proteins in mouse models, suggesting potential therapeutic pathways for humans. Continued research in gene editing for prion disease holds promise for unraveling the complexities surrounding these devastating conditions.
In exploring gene editing’s role in prion protein research, the importance of collaboration stands out. Multidisciplinary partnerships have been pivotal, combining expertise in genetics, neurology, and therapeutics. Innovations in vector engineering are also critical, as researchers seek safer, more effective ways to deliver gene-editing components to the right cells. By leveraging advancements in technology and fostering collaborations, the scientific community aims to bring the revolutionary potential of gene editing into practical applications for individuals affected by prion diseases.
Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel: Pioneers in Prion Research
Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel embody the spirit of patient-scientists in the realm of prion disease research, driving innovative approaches in tackling these fatal conditions. After Vallabh’s diagnosis of fatal familial insomnia, the couple pivoted their careers from law and city planning to neuroscience, committing to a mission to understand and counteract the effects of prion diseases. Their diverse backgrounds enable them to infuse new perspectives into the research process, enhancing not just laboratory techniques but also the emotional and ethical dimensions of scientific inquiry.
Their work in the lab at the Broad Institute stands as a beacon of hope for families affected by prion diseases, as they channel their personal experiences into groundbreaking research. Collaboration with seasoned researchers like David Liu offers a significant advantage, helping to stay at the forefront of therapeutic advancements. The combination of lived experience and scientific rigor empowers them to advocate for ethical and patient-centered research approaches, striving to translate their discoveries into meaningful treatments that could potentially revolutionize the future of prion disease therapy.
The Personal Connection to Prion Disease Research
The narrative around prion diseases often feels distant and abstract, but for researchers like Vallabh and Minikel, it is a deeply personal journey that fuels their passion and dedication. Vallabh’s experience with her mother’s decline due to fatal familial insomnia adds an emotional layer to their scientific endeavors. This connection not only motivates their work but also brings a focused urgency to advance research and eventual treatment options. Such personal investment illustrates that research is not just about the science, but about real lives affected by these complex diseases.
This personal journey extends beyond individual motivation to influence the broader research environment, fostering empathy and understanding among collaborators in the field. Vallabh and Minikel’s collaboration with others amplifies this mission, highlighting the importance of patient input in scientific research. Their story and personal stakes serve as a reminder that behind every research paper and scientific breakthrough are individuals and families waiting for a solution. Continued advancements in prion disease treatments hinge not just on the latest technologies but also on the shared commitment of those involved to find a cure.
Translating Research into Human Trials: Challenges Ahead
Translating promising research findings into human trials presents a formidable challenge, particularly in the context of prion diseases, which are complicated by their infectious nature and the significant risks associated with research. As scientists navigate the regulatory pathways involved in developing gene-editing therapies, they must ensure not only efficacy but also patient safety. The need for meticulous preclinical testing and the ethical considerations surrounding human trials highlight the cautious yet hopeful approach the field must adopt as it advances toward potentially life-saving therapies.
Moreover, the transition from laboratory success to clinical application often involves various challenges, including ensuring reliable delivery mechanisms for gene-editing techniques and addressing potential long-term impacts. Researchers must collaborate closely with regulatory bodies and ethical committees to navigate these hurdles effectively. Despite the challenges, the unwavering determination displayed by scientists like Vallabh and Minikel, coupled with the community’s growing interest in prion disease, may shorten the timeline to successful human trials, opening doors to innovative treatments in the near future.
Funding and Support: Vital Roles in Prion Research
Funding is a vital component in the pursuit of advancements in prion disease research, as financial resources are necessary to support the intricate scientific processes involved. Institutions like the National Institutes of Health and private foundations such as the Prion Alliance play critical roles in providing grants for innovative research projects focused on gene editing and therapeutic interventions. Without adequate funding, the momentum towards developing effective treatments for conditions like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia could significantly slow down, delaying hope for affected individuals.
In addition to traditional funding mechanisms, community support and awareness initiatives are crucial in sustaining prion research. By fostering a broader conversation about rare diseases and their societal impacts, advocates can garner additional resources and attract a diverse pool of researchers to the field. Cultivating strong ties between researchers, funding agencies, and patient advocacy groups creates a robust support system that is essential for ongoing research efforts and ultimately achieving breakthroughs in prion disease treatment.
The Future of Prion Disease Therapeutics
The horizon for prion disease therapeutics is brightening, thanks in part to advancements in gene therapy and collaborative research efforts within the scientific community. As researchers continue to explore the genetic underpinnings of prion diseases and develop innovative techniques, there is a genuine hope that effective treatments may be on the near horizon. The collaborative spirit among laboratories, which includes the integration of insights from patient-scientists, is pivotal in accelerating the development of targeted therapies and ultimately potential cures.
Furthermore, as gene editing technologies evolve, the potential to create specific and efficient targeting mechanisms for prion proteins enhances the possibilities for effective therapeutics. Continued investment in research, alongside the pursuit of ethical and rigorous testing processes, will be essential in translating laboratory discoveries into clinical realities. The future of prion disease treatment promises not just hope for patients but also a testament to the resilience and dedication of researchers working tirelessly to turn breakthroughs into life-saving options.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the latest advancements in prion disease treatment using gene editing?
Recent advancements in prion disease treatment have focused on gene editing techniques, particularly a method developed at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard. Researchers demonstrated that altering a single base in the prion protein gene could reduce the production of toxic proteins in mouse models. This approach led to a significant extension in lifespan, offering hope for future therapies targeting conditions like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia.
How does gene editing help in treating fatal familial insomnia?
Gene editing plays a crucial role in treating fatal familial insomnia by directly targeting the genetic mutations responsible for producing abnormal prion proteins. By utilizing advanced techniques such as base editing, researchers aim to correct these mutations, thereby decreasing protein accumulation in the brain, which could potentially halt disease progression.
Is there a cure for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with current prion therapies?
As of now, there is no known cure for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease; however, recent research into prion therapy advancements suggests that gene editing techniques may provide breakthrough treatment options in the future. Early studies in animal models indicate promising results, but extensive research and human trials are required before any definitive treatment can be established.
What role does prion protein research play in developing new therapies?
Prion protein research is essential for developing new therapies as it helps scientists understand the mechanisms behind prion diseases. This research enables the identification of specific mutations and helps inform the design of targeted gene editing strategies, which could lead to effective treatment options for conditions like fatal familial insomnia and other prion diseases.
What challenges remain in the development of prion disease treatments?
Several challenges remain in the development of effective prion disease treatments, including the transition from successful animal models to human clinical trials. Researchers must refine gene editing techniques to enhance safety and efficacy, ensuring that gene therapies can efficiently target and reduce the production of prion proteins without adverse effects.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Research Team | Led by Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel, focused on gene-editing for prion diseases. |
| Prion Disease Overview | Rare, fatal disorders caused by misfolded brain proteins; includes Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, fatal familial insomnia. |
| Breakthrough Research | Gene-editing showed 50% reduction of harmful proteins in mice, leading to lifespan extension by 52%. |
| Future Trials | Many steps remain before human trials can begin; current research is in early experimental stages. |
| Personal Motivation | Vallabh’s personal connection to prion disease drives the research team’s commitment to finding a treatment. |
Summary
Prion disease treatment is advancing thanks to new research that shows promising results from gene-editing therapies. This innovative approach has demonstrated a significant reduction of harmful proteins in laboratory mice, providing hope for future clinical applications. With continued dedication from researchers like Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel, who are personally affected by these conditions, there is optimism that effective therapies may soon be developed, transforming the landscape of treatment options for prion diseases.