Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease is crucial in managing this devastating neurodegenerative condition before significant cognitive impairment sets in. Recent research highlights the significance of an innovative olfactory testing method that can be easily performed at home, acting as an effective Alzheimer’s risk assessment tool. Participants engage in simple cognitive impairment tests that measure their ability to identify and remember different scents, revealing early signs of cognitive decline. This groundbreaking approach aims to empower individuals by providing accessible means for Alzheimer’s early detection, allowing for timely interventions. By harnessing these new insights, we can tackle the onset of Alzheimer’s and enhance overall brain health.
Proactively recognizing the initial symptoms of memory loss and cognitive dysfunction associated with Alzheimer’s is essential for effective intervention and care. This novel approach to Alzheimer’s risk indicators uses scent-based assessments, offering a user-friendly solution for identifying potential cognitive deterioration in the comfort of one’s home. Moreover, comprehending the nuances of neurodegenerative disease onset through methods like olfactory testing could transform current practices in identifying at-risk individuals. Utilizing at-home screening tools not only facilitates early identification but also opens avenues for further cognitive research, which is paramount as we strive to develop more effective treatment protocols for age-related cognitive decline. As public awareness grows, the importance of engaging in these assessments becomes more vital in safeguarding cognitive health for older adults.
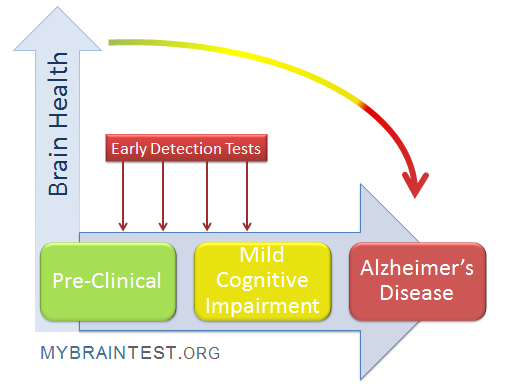
Understanding Alzheimer’s Early Detection Methods
Detecting Alzheimer’s disease in its early stages is crucial for effective intervention and treatment. Recent advancements in cognitive impairment tests, particularly the innovative olfactory test developed by researchers at Mass General Brigham, highlight the potential for early detection. This noninvasive test is designed to be performed at home, allowing individuals to assess their olfactory function—an important indicator of cognitive health. The ability to identify, discriminate, and remember odors has been shown to decline in older adults experiencing cognitive impairment, forming a basis for risk assessment of conditions like Alzheimer’s.
Incorporating olfactory testing into routine health assessments can enable healthcare professionals to identify individuals at risk of Alzheimer’s even before notable symptoms appear. With the rise of at-home testing options and increasing awareness of neurodegenerative disease signs, such methods can empower patients and healthcare providers alike. Early detection not only aids in planning for future cognitive health challenges but also opens avenues for preemptive treatments and lifestyle changes that can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life.
The Role of Olfactory Testing in Alzheimer’s Risk Assessment
Olfactory testing serves as a critical component in Alzheimer’s risk assessments. By evaluating an individual’s ability to perceive and identify odors, researchers can gain insights into their cognitive health. The olfactory function acts as a sensitive marker that can indicate early changes in the brain associated with Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. The study conducted at Mass General Brigham found that individuals with mild cognitive impairment showcased notable differences in test results compared to those without cognitive issues, reinforcing the significance of smell as a predictor.
The efficacy of olfactory tests in assessing Alzheimer’s risk could revolutionize early detection methods. The simplicity of these tests makes them accessible for widespread use, potentially allowing for large-scale screenings. As a result, not only can individuals take charge of their cognitive health through at-home tests, but these assessments may also contribute to valuable data that can drive research and inform treatment protocols for Alzheimer’s disease. By focusing on olfactory dysfunction, healthcare providers can tailor interventions to those most at risk, improving patient outcomes.
Cognitive Impairment Tests: A Comprehensive Approach
Cognitive impairment tests encompass a variety of assessments designed to evaluate mental function and memory. These tests, including the recently highlighted olfactory assessments, aim to establish baseline cognitive health and identify potential declines over time. The integration of various testing methods provides a thorough understanding of an individual’s cognitive abilities and can assist in diagnosing conditions such as Alzheimer’s. This comprehensive approach is essential in ensuring timely intervention and support for individuals encountering signs of neurodegenerative diseases.
Incorporating cognitive impairment tests like the olfactory test into regular health evaluations can enhance early detection strategies. As Alzheimer’s disease continues to affect millions worldwide, understanding the subtleties of cognitive decline becomes paramount. These tests not only serve as diagnostic tools but also facilitate ongoing monitoring of cognitive health, providing insights into the effectiveness of treatment plans or lifestyle changes that may prevent further decline.
The Significance of At-Home Alzheimer’s Tests
At-home Alzheimer’s tests represent a significant advancement in managing cognitive health, allowing individuals to proactively monitor their abilities in the comfort of their homes. The olfactory testing method, developed as part of a broader research initiative, empowers users to assess their cognitive function without the need for immediate clinical intervention. This accessibility is particularly beneficial for older adults who may find it challenging to navigate traditional healthcare settings.
Furthermore, at-home Alzheimer’s tests can reduce the stigma associated with cognitive decline. By promoting routine testing as a normal part of health care, individuals may feel emboldened to seek assistance without fear of embarrassment. Early intervention through at-home testing can lead to timely medical consultations and potential lifestyle adjustments that may enhance cognitive longevity. Ultimately, the shift towards home-based testing is poised to play a pivotal role in the landscape of Alzheimer’s disease research and patient care.
Olfactory Dysfunction as an Early Warning Sign
Research suggests that olfactory dysfunction can serve as an early indicator of cognitive decline, potentially signaling the onset of diseases such as Alzheimer’s. The loss of smell often goes unnoticed until significant cognitive symptoms develop, making it a crucial area of focus for early detection strategies. By incorporating olfactory testing alongside cognitive impairment assessments, clinicians can identify at-risk individuals before typical signs of dementia manifest.
The implications of using olfactory dysfunction as a screening tool are substantial. Early identification allows for proactive management and intervention strategies, including lifestyle changes and therapeutic options that may slow disease progression. Furthermore, this approach aligns with a growing emphasis on personalized medicine, tailoring recommendations based on individual risk profiles and cognitive health history. Utilizing olfactory tests could thus shape future methodologies for Alzheimer’s prevention and care.
Research Advancements in Neurodegenerative Disease Testing
The field of neurodegenerative disease research is evolving rapidly, with innovative testing methods transforming how we understand and detect conditions such as Alzheimer’s. Studies exploring the link between olfactory function and cognitive decline have paved the way for new diagnostic criteria that prioritize early indicators. As researchers continue to refine these tests, the potential for widespread clinical applications becomes increasingly viable.
Ongoing research is crucial in validating the efficacy of these tests and establishing standardized protocols for their implementation in clinical settings. By leveraging tools like olfactory testing, the medical community can take significant strides toward early detection and intervention for neurodegenerative diseases. Improved diagnostic technologies not only enhance our understanding of these conditions but also empower patients to engage in their health care actively.
Future Directions in Alzheimer’s Disease Research
The future of Alzheimer’s disease research holds great promise as scientists explore innovative techniques for early detection and intervention. The development of olfactory tests, as demonstrated by the work of researchers at Mass General Brigham, exemplifies a shift towards more accessible and user-friendly screening methods. This evolution reflects a broader trend in medicine where patient-centered approaches are becoming paramount, enabling individuals to take charge of their health outcomes.
Future studies will likely delve deeper into the relationship between olfactory function and cognitive decline, aiming to refine testing protocols and integrate them into routine health assessments. Additionally, the potential for these tests to be used in multiple languages enhances their applicability across diverse populations, making them a valuable tool in global health initiatives. Ultimately, advancing Alzheimer’s research aims to unlock new preventative strategies that can dramatically improve the quality of life for those affected by cognitive impairments.
Implications of Early Alzheimer’s Detection for Caregiving
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease is not only crucial for patients but also for their caregivers. Understanding the potential risks through tests such as olfactory assessments enables families to prepare for the journey ahead. Caregiving can be profoundly challenging, and being informed about the status of a loved one’s cognitive health can facilitate critical decisions concerning care options, support resources, and overall planning.
Moreover, caregivers equipped with knowledge about early symptoms are better positioned to advocate for their loved ones’ needs within the healthcare system. They can initiate conversations with medical professionals, seek out appropriate interventions, and access resources designed to assist both the individual with Alzheimer’s and their caregivers. Ultimately, early detection can foster a supportive environment where proactive measures are taken, enhancing the overall experience for both patients and those who care for them.
Educating the Public on Alzheimer’s Disease Awareness
Public awareness and education play a pivotal role in the fight against Alzheimer’s disease. Understanding the risk factors, signs, and available testing options can empower individuals to seek help and reduce the stigma surrounding cognitive decline. Initiatives aimed at increasing knowledge about Alzheimer’s often highlight the importance of early detection through various methods, including cognitive impairment tests and olfactory assessments.
Community education can promote the adoption of at-home testing kits and encourage discussions about cognitive health among families. Efforts to reach diverse populations, including resources in different languages, ensure that information is accessible to everyone. By fostering a well-informed community, we can enhance early detection rates and support ongoing research efforts aimed at finding innovative solutions to combat Alzheimer’s disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Alzheimer’s early detection through cognitive impairment tests?
Alzheimer’s early detection through cognitive impairment tests involves assessing memory and cognitive functions to identify individuals at risk. These tests help in recognizing early signs of Alzheimer’s, allowing for timely interventions. Studies have shown that tests evaluating odor discrimination and identification may reveal cognitive impairments that precede visible symptoms.
How does olfactory testing help in the early detection of Alzheimer’s?
Olfactory testing is a promising method for Alzheimer’s early detection. Research indicates that a decline in the sense of smell can signify neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. Participants who struggle with odor memory tasks may be at higher risk, making this a valuable tool in assessing Alzheimer’s risk prior to clinical symptoms.
Can I perform an at-home Alzheimer’s test to assess my risk?
Yes, at-home Alzheimer’s tests, like the olfactory test, are designed to be easy to administer. These tests can help individuals evaluate their cognitive functions and identify potential risks of Alzheimer’s disease. Tools are available that measure abilities like odor identification as a part of Alzheimer’s risk assessment.
What are the signs of neurodegenerative diseases detectable through Alzheimer’s early detection tests?
Signs of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s include decreased memory, difficulty in odor discrimination, and cognitive decline. Tests assessing these functions can be crucial for early detection, showing how a decline in these areas could indicate a higher risk for developing Alzheimer’s.
What is the significance of Alzheimer’s risk assessment in cognitive health?
Alzheimer’s risk assessment through cognitive tests is vital for early intervention strategies. Identifying cognitive impairment or olfactory dysfunction allows healthcare providers to implement preventive measures and monitor cognitive health, potentially delaying the onset of Alzheimer’s symptoms.
Are olfactory tests effective for Alzheimer’s early detection across different languages and cultures?
Research indicates that olfactory tests are effective for Alzheimer’s early detection across various languages and cultures. Studies involving English and Spanish-speaking participants show consistent results, suggesting that olfactory testing can be a universally applicable tool in assessing cognitive impairment related to Alzheimer’s.
How do I know if I need cognitive impairment testing for Alzheimer’s?
If you or a loved one experiences memory issues, difficulty concentrating, or olfactory changes, consider cognitive impairment testing for Alzheimer’s. Early detection enabled by these tests can lead to better management options and enhance the quality of life.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Early Detection Importance | Identifying cognitive impairment early can help in treating Alzheimer’s before symptoms surface. |
| Olfactory Test Development | Researchers from Mass General Brigham created a home-based olfactory test to assess smell discrimination, identification, and memory as indicators of cognitive impairment. |
| Test Results | Older adults with cognitive impairment scored lower on the olfactory test compared to cognitively normal individuals, indicating a potential early warning sign for Alzheimer’s. |
| Participant Demographics | The study included English- and Spanish-speaking participants with cognitive complaints, ensuring diverse representation. |
| Future Research Directions | Future studies may integrate neuropsychological testing and longitudinal patient follow-ups to enhance predictive capabilities for cognitive decline. |
Summary
Alzheimer’s early detection is a crucial aspect of preventive healthcare. Recent research has shown that olfactory tests, which evaluate smell identification and discrimination, can serve as effective early indicators of cognitive impairment, potentially allowing for interventions long before the onset of significant memory issues. As scientists continue to refine these tests and explore their predictive power, they pave the way for improved strategies in Alzheimer’s treatment and early intervention.