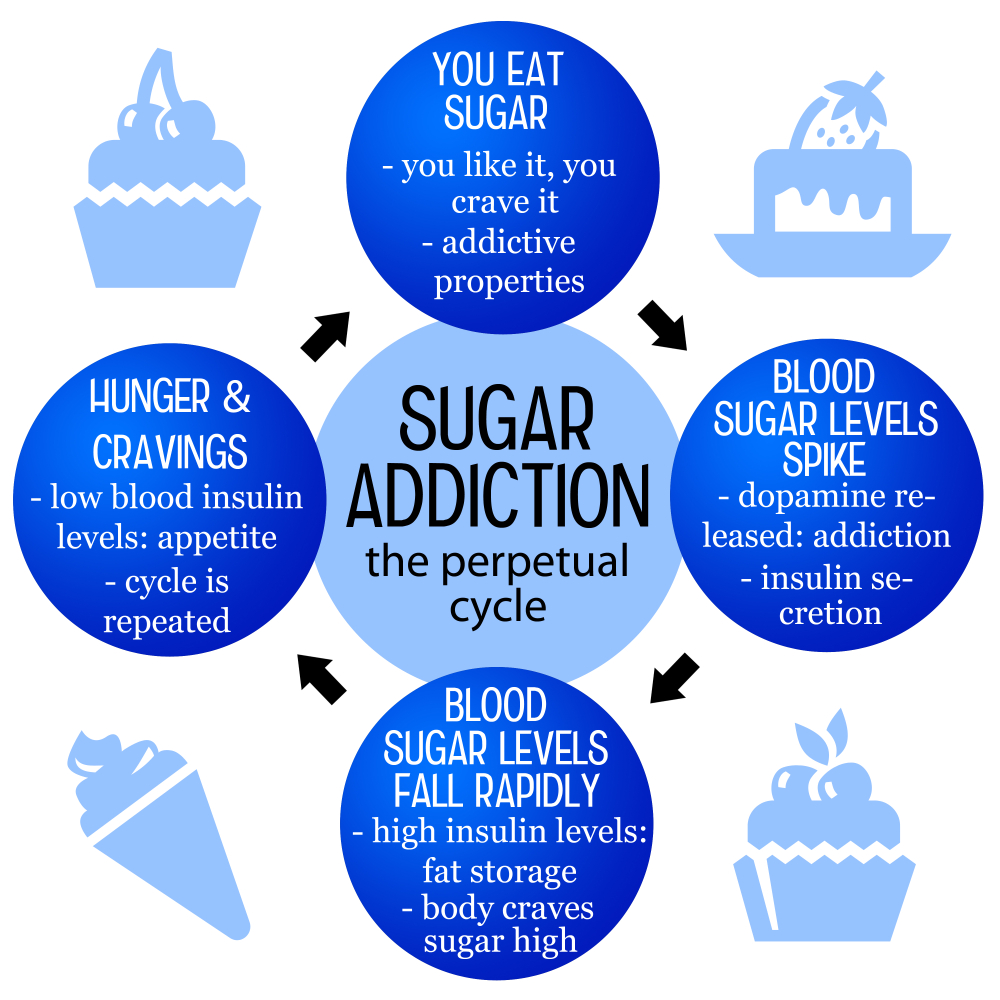
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked considerable debate among experts in nutrition and health. While sugar definitely promotes cravings and can lead to compulsive eating behaviors, it does not meet the strict clinical criteria used to classify substances like alcohol and nicotine as addictive. Our diets are often filled with processed foods high in added sugars, which can intensify cravings and contribute to habitual overconsumption. Understanding the health effects of sugar and adhering to sugar intake recommendations is crucial for managing consumption and promoting overall well-being.
When discussing the potential addictive nature of sugar, it is essential to consider terms like sugar cravings and impulsive eating. Many individuals find themselves reaching for sweets, driven by a desire for pleasurable, rewarding foods, which can lead to a cycle of consumption and withdrawal-like symptoms. Ultra-processed snacks and beverages, laden with unhealthy components, can exacerbate the issue, creating an environment where people struggle to manage their intake. While some experts draw parallels between sugar and other addictive substances, the reality is that sugar occupies a unique space in our diets, where moderation, rather than complete elimination, is key to a balanced approach.
Is Sugar Addictive? The Ongoing Debate
The question of whether sugar is addictive or not has stirred considerable debate among scientists and nutritionists alike. While substances like alcohol and nicotine meet strict clinical definitions of addiction, sugar doesn’t quite fit into this category. However, many report experiencing strong cravings and compulsive behaviors related to sugar, which are often similar to reactions associated with addictive substances. In ultra-processed foods, sugar intermingles with unhealthy fats and sodium, enhancing their palatability and making it challenging for individuals to resist these products. This phenomenon creates a cycle of habitual consumption where the sudden cessation of such foods can provoke withdrawal-like symptoms including headaches, anxiety, and irritability.
On a biochemical level, sugar acts in the brain’s reward pathways much like addictive substances do. This can lead to a conditioned response where the brain craves more sugar, especially when heavily processed foods high in sugar are readily accessible. Yet, it’s essential to clarify that while sugar might evoke ‘addictive-like’ behaviors, it is inherently different from substances that have no beneficial nutritional value. A moderate intake of sugar, particularly from natural sources like fruits and whole grains, can be part of a balanced diet. Acknowledging this difference is crucial in promoting healthier dietary choices without categorizing sugar in the same risk bracket as alcohol or drugs.
Understanding Sugar Cravings and How to Manage Them
Sugar cravings can often feel overpowering, influenced by our biological makeup and the modern food environment rich in processed snacks and desserts. When people consume these sugar-packed foods regularly, their bodies become accustomed to high sugar levels, leading to stronger cravings over time. This habitual consumption not only reinforces the desire for more sugar but can also result in negative health consequences, such as obesity and diabetes. Therefore, understanding and managing sugar cravings is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Simple strategies, such as gradually reducing sugar intake and opting for natural sugars found in fruits, can help mitigate these cravings over time.
Moreover, recognizing the psychological triggers behind sugar cravings is a vital aspect of managing them. Emotional eating, stress, and fatigue can all lead individuals to seek comfort in sugary foods. By being mindful of these triggers, one can develop healthier coping mechanisms that do not rely on sugar. Practical options may include practicing mindfulness, engaging in physical activity, or having nutritious snacks on hand that satisfy sweet cravings without the extensive sugar load. This balanced approach can prevent the feelings of deprivation that often accompany drastic dietary changes and promote long-term wellness.
Effects of Sugar on Physical and Mental Health
The health effects of sugar, particularly added sugars found in processed foods, are of great concern to nutritionists and health professionals. Excessive sugar intake has been linked to various health issues, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar consumption to maximize health benefits but finds many individuals overshooting these guidelines. For example, the average American consumes about 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, which is significantly above the recommended levels of 6 teaspoons for women and 9 for men. This high intake can contribute not just to physical ailments but also to negative psychological effects, including mood swings and increased anxiety.
On the positive side, consuming sugar in moderation plays an important role within a balanced diet. Naturally occurring sugars, such as those in fruits and vegetables, provide essential nutrients alongside sweetness, promoting better health outcomes. It’s crucial, however, to be discerning about the sources of sugar in one’s diet. While the satisfaction of taste buds is vital, the overall quality of the diet should take precedence to ensure that sugar contributes positively to physical and mental well-being. Awareness of sugar’s role in the diet promotes more conscious eating habits and aids individuals in making better choices.
Recommended Sugar Intake for a Healthy Lifestyle
Managing sugar intake through informed choices is essential for fostering a healthier lifestyle. The American Heart Association’s recommendations reflect a growing concern over high sugar consumption, suggesting that individuals aim for limits of no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women. For children, even lower limits are advocated to help cultivate healthy eating habits early on. By adhering to these guidelines and being mindful of added sugars hidden in many processed foods, people can reduce overall sugar intake and avoid the potential health risks associated with excess consumption.
In addition to adhering to these recommendations, it’s vital for individuals to pay close attention to food labels. Many seemingly healthy options may contain high levels of added sugars that can contribute to excess caloric intake. Gradually reducing sugar consumption instead of making abrupt changes can also prevent feeling deprived, which might lead to binge eating later on. Incorporating wholesome alternatives and natural sweeteners can make the transition easier while still satisfying sweet cravings. In doing so, individuals can enjoy their favorite flavors without compromising their health.
The Role of Processed Foods in Sugar Consumption
Processed foods significantly contribute to the high sugar consumption observed in modern diets. The convenience and low cost of pre-packaged snacks and sugary drinks make them accessible and tempting. These foods often contain not only added sugars but also unhealthy fats and sodium, creating a perfect storm for weight gain and various health issues. Understanding the extent of sugar present in these processed items is essential for making healthier eating choices, and education plays a crucial role in this understanding.
Making conscious decisions about food choices is paramount in combatting the pervasive influence of processed foods. By choosing whole and minimally processed foods instead, individuals can better control their sugar intake. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins offers essential nutrients and keeps sugar levels in check. More importantly, it promotes satiety and reduces the likelihood of succumbing to cravings. Empowering individuals with knowledge about food ingredients and health impacts will aid in fostering better dietary habits.
Strategies to Curb Sugar Cravings
Curbing sugar cravings requires strategic approaches that focus on both dietary choices and behavioral adjustments. One effective strategy is incorporating more fiber into meals, as fiber-rich foods can naturally reduce cravings by promoting a feeling of fullness. Foods like legumes, whole grains, and fruits contribute not only nutrients but also help stabilize blood sugar levels. Maintaining steady energy levels throughout the day lessens the temptation to reach for sugary snacks.
Moreover, hydration is often overlooked in the conversation about sugar cravings. Dehydration can sometimes mimic feelings of hunger, leading to unnecessary snacking on sugary items. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can alleviate this false hunger signal and reduce sugar cravings. Additionally, planning meals and snacks ahead of time can prevent impulsive choices when cravings strike, ultimately supporting a more balanced approach to sugar consumption.
Breaking the Habit: Reducing Added Sugar Over Time
Changing dietary habits, particularly reducing added sugars, can seem daunting but is achievable when approached incrementally. Rather than attempting to eliminate sugar completely, which may backfire and lead to increased cravings, individuals should focus on gradual reduction. This might include cutting back on sugary beverages, choosing unsweetened alternatives, or using smaller amounts of added sugar in cooking and baking. Over time, these small changes can result in significant reductions in overall sugar intake.
Setting realistic goals can also make the process more manageable. For instance, individuals can challenge themselves to go one week without purchasing processed foods rich in added sugars. This can create awareness of consumption patterns and motivate healthier choices. Support groups or community resources can further aid in this journey by providing encouragement and sharing ideas. The ultimate goal is to cultivate a healthier relationship with sugar, one that allows for enjoyment without compromising health.
Mindfulness in Eating: Avoiding Sugar Overconsumption
Mindful eating is becoming increasingly recognized as an effective strategy to combat sugar overconsumption. This practice encourages individuals to pay close attention to their food choices, savoring each bite and recognizing hunger cues. By being more aware of the flavors and textures of what they eat, it becomes easier to find satisfaction without the need for excessive sugar. Being present during meals can also enhance the overall eating experience, steering focus away from impulsive decisions.
Incorporating mindfulness techniques into daily routines can be beneficial beyond just eating practices. By reflecting on emotional triggers and occurrences during sugar cravings, individuals can learn to react differently in those moments. Techniques such as meditation, journaling, or guided reflections can help process these triggers effectively. This holistically addresses sugar cravings without relying solely on willpower or deprivation, resulting in a more balanced and healthy lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like other substances?
While sugar can trigger cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. However, the impact of sugar on your brain’s pleasure centers can lead to repetitive consumption, especially from processed foods that are high in sugar.
What are the health effects of sugar and its addictive qualities?
Sugar, particularly when consumed in high amounts through processed foods, can lead to health issues such as obesity and diabetes. Although it may have addictive qualities, moderate sugar intake is necessary for health, and balance is key.
How can I manage sugar cravings effectively?
To manage sugar cravings, gradually reduce your intake of added sugars and focus on whole foods. Pairing healthy snacks with protein and fiber can help stabilize blood sugar levels and minimize cravings.
What are the recommendations for sugar intake to avoid addiction risks?
The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar intake to no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women per day. Staying within these guidelines can help mitigate the potential risks of sugar dependence.
Are processed foods more addictive due to sugar content?
Yes, processed foods often contain high levels of added sugars, which can enhance their palatability and lead to increased cravings. This can result in habitual consumption patterns, making it harder to reduce sugar intake.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Sugar is not classified as an addictive substance clinically like alcohol or nicotine, though it can trigger cravings and compulsive behaviors. |
| The modern diet is full of ultra-processed foods high in sugar, fats, and sodium, which amplify cravings and can lead to habitual consumption. |
| Withdrawal-like symptoms may occur when reducing sugar intake, including headaches and anxiety, but these symptoms are milder than with true addictive substances. |
| Moderate amounts of sugar are necessary for diet balance and can enhance the enjoyment of food, making outright elimination potentially counterproductive. |
| The average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, exceeding recommended limits of 9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked debate among nutrition experts. While sugar does not meet the clinical criteria for addiction like alcohol or nicotine, it certainly can elicit cravings and compulsive eating behaviors. The prevalence of ultra-processed foods high in sugar contributes to these cravings, making it challenging for many to reduce sugar intake. Withdrawal-like symptoms are real but less severe than those experienced with true addictive substances. With moderate amounts of sugar being beneficial for flavor and diet, the focus should instead be on consuming sugar responsibly, being aware of daily intake, and gradually reducing added sugars from your diet without entirely eliminating them.