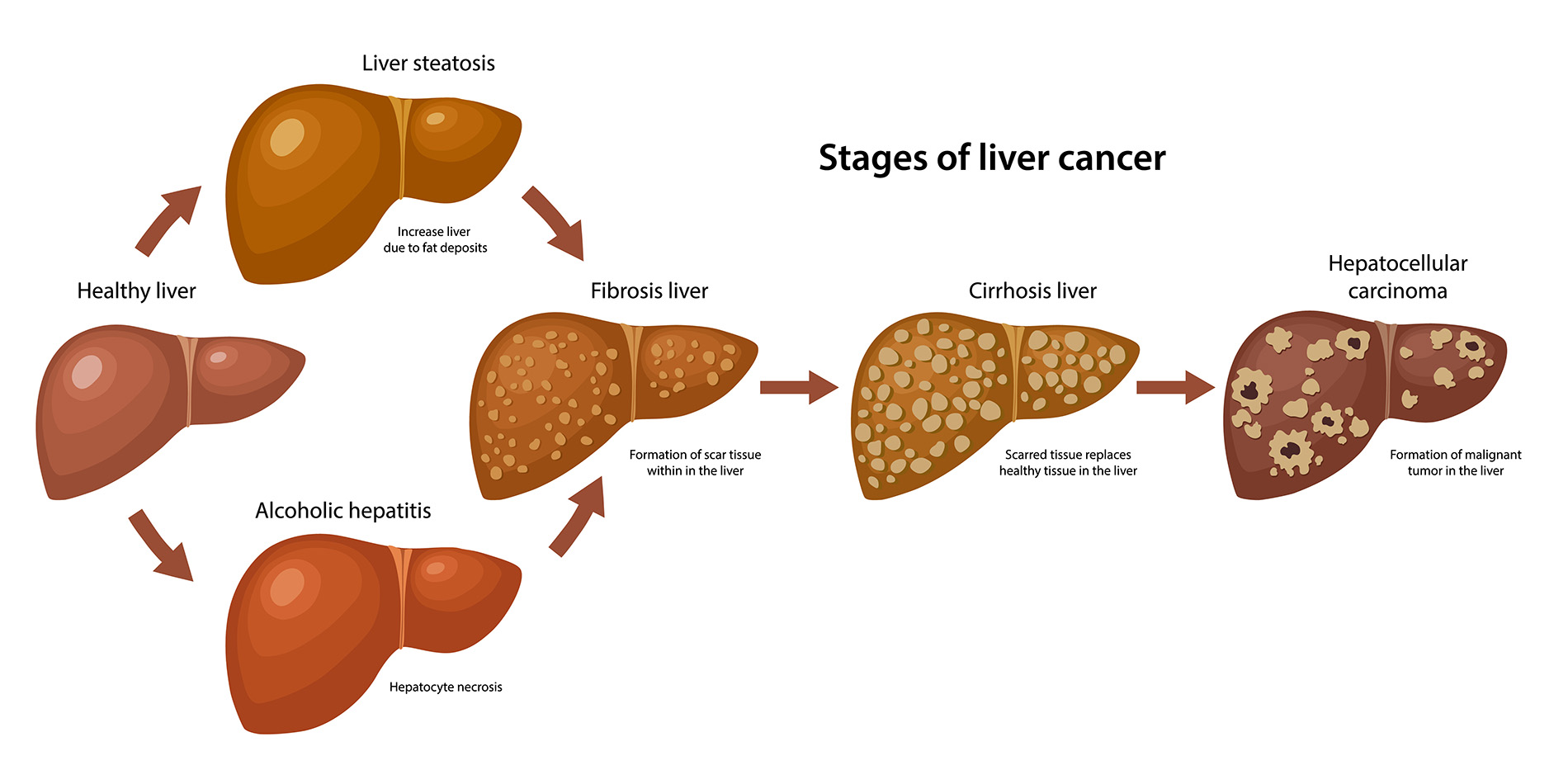
Bile imbalance liver cancer is a pressing concern as recent studies reveal a direct correlation between disrupted bile acid metabolism and the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the predominant form of liver cancer. This critical imbalance can lead to inflammation and fibrosis in the liver, ultimately paving the way for cancerous growths. Researchers have identified FXR receptors as vital components involved in regulating bile acids, highlighting the importance of these metabolic pathways in liver disease treatments. Furthermore, insights into the YAP signaling pathway have uncovered new potential therapeutic targets in combating liver cancer. Understanding the intricacies of bile acid metabolism is crucial for developing innovative strategies to prevent and treat conditions related to bile imbalance liver cancer and improve patient outcomes.
The issue of dysregulated bile production, often referred to as bile acid imbalance, has significant implications for liver health, particularly concerning the risk of liver tumors. This phenomenon is intricately linked to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma, where improper regulation of bile acids plays a critical role. By exploring alternative terminology—such as bile acid dysregulation and liver-related malignancies—healthcare professionals are uncovering new dimensions of how metabolic disturbances can influence liver disease. Additionally, advancements in understanding the roles of FXR receptors and the YAP signaling pathway may enhance liver disease treatments, providing pathways for more effective clinical interventions. Overall, grasping the connections between bile imbalance, liver cancer, and their underlying mechanisms is vital for improving therapeutic approaches.
Understanding Bile Acid Metabolism in Liver Health
Bile acid metabolism is crucial for maintaining liver health and overall metabolic balance. Produced by the liver, bile acids assist in the digestion of fats while also serving regulatory roles in diverse physiological functions. An imbalance in these bile acids can lead to serious liver conditions, including liver inflammation and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recent research has underscored the importance of maintaining bile acid homeostasis through various signaling pathways, including the FXR receptors, which play a pivotal role in regulating bile acid synthesis and transport.
Disruptions in bile acid metabolism trigger a cascade of health complications. The liver’s inability to properly regulate bile acids can culminate in excessive accumulation, leading to cellular damage and liver diseases. The FXR receptors, when functioning optimally, help to restore balance by regulating gene expression related to bile acid synthesis and transport. Understanding these mechanisms offers potential therapeutic avenues for preventing liver disease progression and developing effective treatments.
The Link Between Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer
Studies have increasingly highlighted the link between bile acid imbalance and the development of liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The accumulation of bile acids due to dysfunctional FXR receptor activity can induce liver injury and inflammation, laying the groundwork for malignancy. When bile acids are not effectively excreted, they contribute to a toxic environment within the liver that promotes oncogenic processes. It’s critical to investigate and understand these pathways to devise preventive strategies against liver cancer.
Recent findings indicate that YAP (Yes-associated protein) signaling plays a significant role in the regulation of bile acid metabolism and may enhance the risk of developing liver cancer. As YAP represses essential functions of FXR, blocking this pathway could potentially mitigate the harmful effects of bile acid overload. Therapeutic interventions targeting YAP and enhancing FXR function might provide a promising approach to curb liver cancer related to bile imbalance.
The Role of FXR Receptors in Liver Disease
FXR receptors are integral to maintaining bile acid homeostasis and thus play a critical role in liver health. These nuclear receptors are activated by bile acids and help regulate their synthesis and transport within the liver. A malfunction in FXR signaling can lead to an excess accumulation of bile acids, contributing to cellular stress and liver disease. Therefore, targeting FXR can be a key strategy in developing new treatments aimed at preventing liver damage and diseases associated with bile acid dysregulation.
Recent research has shown that pharmacological activation of FXR can alleviate liver inflammation and fibrosis, thereby reducing the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). By enhancing FXR function, we can potentially improve bile acid metabolism and reverse the pathogenic cycles initiated by bile acid imbalance. The ongoing exploration of FXR as a therapeutic target opens avenues for innovative liver disease treatments that could significantly improve patient outcomes.
Mechanisms of YAP Signaling in Liver Cancer Progression
The YAP signaling pathway has emerged as a critical modulator in liver cancer progression, especially in relation to bile acid metabolism. Contrary to its anticipated role in promoting cell growth, YAP acts as a repressor of FXR, leading to impaired bile acid homeostasis. This unexpected role of YAP can exacerbate liver damage, inflammation, and subsequently increase the risk of developing HCC. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for identifying therapeutic interventions that can disrupt this damaging cycle.
By targeting the YAP pathway, researchers hope to find effective strategies to restore normal FXR function and balance bile acid levels in the liver. Inhibiting YAP’s repressive activity or promoting bile acid excretion has shown promise in experimental models, suggesting that this could be a viable approach for preventing liver cancer progression. Delving deeper into the relationship between YAP signaling and bile acid metabolism could unveil novel targets for therapeutic intervention.
Investigating Liver Disease Treatments Through Bile Acid Regulation
Current strategies for treating liver diseases often revolve around restoring the balance of bile acids and enhancing liver function. Understanding the molecular pathways involved in bile acid metabolism, particularly the role of FXR and YAP, can lead to novel therapeutic approaches. Interventions aimed at enhancing bile acid excretion or pharmacologically activating FXR may provide significant benefits in treating liver diseases associated with bile acid imbalance.
Moreover, research into liver disease treatments should consider the potential of combined therapies that target both bile acid homeostasis and tumor signaling pathways. By addressing the multifaceted nature of liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma, such approaches could offer improved outcomes for patients struggling with liver health issues. The exploration of these interactions is crucial for developing effective disease management strategies.
The Importance of Early Detection in Liver Cancer
Early detection of liver cancer, especially hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is imperative for improving survival rates. Understanding the risk factors, such as bile acid imbalance, can enhance early diagnostic strategies, enabling proactive management of liver health. Routine screening and the monitoring of bile acids, along with the assessment of FXR and YAP signaling pathways, could serve as valuable tools in identifying at-risk populations.
Furthermore, educating healthcare professionals about the implications of bile acid dysregulation in liver cancer can facilitate timely intervention. By promoting awareness of these biochemical markers, clinicians can better navigate treatment options and preventive strategies, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes in liver disease management.
Potential Pharmacological Solutions for Liver Cancer
The discovery of a molecular switch that regulates bile acid metabolism presents promising avenues for pharmacological interventions in liver cancer treatment. Researchers are exploring various compounds that could enhance FXR function, thereby restoring the homeostasis of bile acids and mitigating liver cancer risk. These pharmacological solutions could provide new hope for patients battling hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting the pathways that contribute to bile imbalance.
Additionally, the disruption of the YAP signaling pathway represents another exciting area of research. Agents that inhibit YAP’s repressive action or enhance bile acid export mechanisms hold significant potential for reducing liver damage and cancer progression. As the scientific community delves deeper into these therapeutic targets, the prospect of developing targeted treatments for liver cancer seems increasingly attainable.
The Future of Liver Disease Research
Moving forward, liver disease research must continue to focus on the intricate relationships between bile acid metabolism, cellular signaling pathways, and cancer development. The intersecting functions of FXR, YAP, and bile acids play a crucial role in understanding liver pathophysiology. Continued research efforts will be essential for unlocking the complexities of these interactions and translating findings into clinical applications.
Future studies should emphasize the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration, integrating insights from molecular biology, pharmacology, and clinical medicine. By fostering such collaborative research environments, we can accelerate the pace of discovery and innovate more effective treatments for liver diseases, ultimately reducing the burden of conditions like hepatocellular carcinoma.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the connection between bile imbalance and liver cancer?
Bile imbalance is linked to liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), as identified in recent studies. Disruptions in bile acid metabolism can lead to liver injury and inflammation, which are critical precursors to the development of liver cancer. The imbalance prompts overproduction of bile acids, increasing the risk of fibrosis and tumor formation.
How do bile acids influence the development of hepatocellular carcinoma?
Bile acids play a significant role in regulating cellular functions and metabolism. An imbalance can disrupt bile acid homeostasis through various pathways, including the FXR receptor. The overproduction of bile acids due to FXR dysfunction can contribute to chronic inflammation and ultimately lead to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
What role do FXR receptors play in bile acid metabolism related to liver disease?
FXR receptors are crucial for maintaining bile acid homeostasis. They regulate bile acid metabolism, and their dysfunction can lead to an imbalance that results in liver disease. In the context of liver cancer, the blockage of FXR by YAP signaling suppresses its function, leading to excess bile acids that drive liver cancer progression.
Can treatments targeted at bile acid metabolism help in liver disease?
Yes, treatments that target bile acid metabolism have potential in managing liver diseases. Pharmacological strategies that stimulate FXR receptor activity or enhance bile acid excretion could help restore balance, reduce liver damage, and slow the progression of diseases like hepatocellular carcinoma.
What is the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway and its significance in liver cancer?
The Hippo/YAP signaling pathway is critical for regulating cell growth and tissue homeostasis. In liver cancer, YAP promotes tumor formation while also influencing bile acid metabolism. Its activation interferes with FXR function, leading to impairments in bile acid regulation and contributing to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma.
What future treatments are being explored based on bile acid metabolism and liver cancer research?
Ongoing research is focusing on pharmacological solutions that enhance FXR function in bile acid metabolism. By stimulating FXR or inhibiting the YAP pathway, these approaches aim to restore normal bile acid levels and mitigate liver damage, offering exciting potential treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance | Disruption in bile acid metabolism can lead to liver diseases including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). |
| Role of YAP | YAP promotes tumor formation by interfering with FXR function, leading to bile acid overproduction. |
| FXR Importance | FXR is crucial for maintaining bile acid homeostasis; its compromise leads to fibrosis and liver cancer. |
| Potential Treatments | Enhancing FXR function or promoting bile acid excretion can reduce liver damage and cancer progression. |
| Research Significance | The findings could lead to pharmacological solutions that stimulate FXR, presenting new treatment avenues. |
Summary
Bile Imbalance Liver Cancer is a critical area of research that illuminates how disruptions in bile acid metabolism can lead to severe liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Current studies highlight the pivotal role of the YAP protein in this dynamic, revealing that it not only contributes to tumor formation but also disrupts the essential functions of bile acid regulation mediated by FXR. With ongoing research exploring potential treatments that can enhance FXR function or improve bile acid excretion, there is promising hope for developing effective interventions against liver cancer.